Abstract
Microplastics (MPs) are emerging environmental pollutants that are present in aquatic environments and accumulate within the food chain, posing significant threats to human health. Over 8 million tons of MPs enter these ecosystems annually. However, existing rapid qualitative and quantitative analytical methods for trace MPs are limited, hindering comprehensive research on their impact in water environments. This study presents a novel composite membrane with both adsorption and filtration functions, integrated with surface enhanced-Raman scattering technology for detecting trace MPs in water. The silver dendrites, modified with n-hexanethiol and loaded onto filter paper, facilitate enhanced enrichment and simultaneous sensitive detection of MPs. The composite membrane exhibited excellent retention rates for standard polystyrene (PS) MPs of various sizes (200, 500, and 1000 nm), achieving high enrichment efficiency. Sensitive detection was realized with a linear response in a concentration range of 0.01 to 0.5 g/L, yielding optimal enhancement factors exceeding 2.92 × 103, enabling detection at μg/L levels. Recovery rates for PS in spiked environmental water samples ranged from 96.86 % to 102.96 %. This innovative method offers a promising approach for the rapid and sensitive detection of trace MPs in aquatic environments, contributing significantly to the assessment of MPs pollution.
中文摘要:
微塑料(microplastics, MPs)是新兴的环境污染物,广泛存在于水生环境中,并可在食物链中累积,对人类健康构成重大威胁。每年有超过800万吨的MPs进入这些生态系统。然而,现有的痕量MPs的快速定性和定量分析方法有限,阻碍了对其在水环境中影响的全面研究。本研究提出了一种具有吸附和过滤功能的新型复合膜,该膜与表面增强拉曼散射技术相结合,用于检测水中的痕量MPs。经过正己硫醇修饰并加载到滤纸上的银枝晶促进了MPs的高效富集和灵敏检测。该复合膜对不同尺寸(200、500和1000 nm)的标准聚苯乙烯(PS)微球表现出优异的截留率,实现了高效富集。在0.01至0.5 g/L的浓度范围内表现出良好的线性关系,最佳增强因子超过2.92 × 10³,检测限达到了μg/L水平。加标环境水样中PS的回收率为96.86%至102.96%。这一创新方法为水环境中痕量MPs的快速灵敏检测提供了一种有前景的方法,对MPs污染的评估具有重要意义。
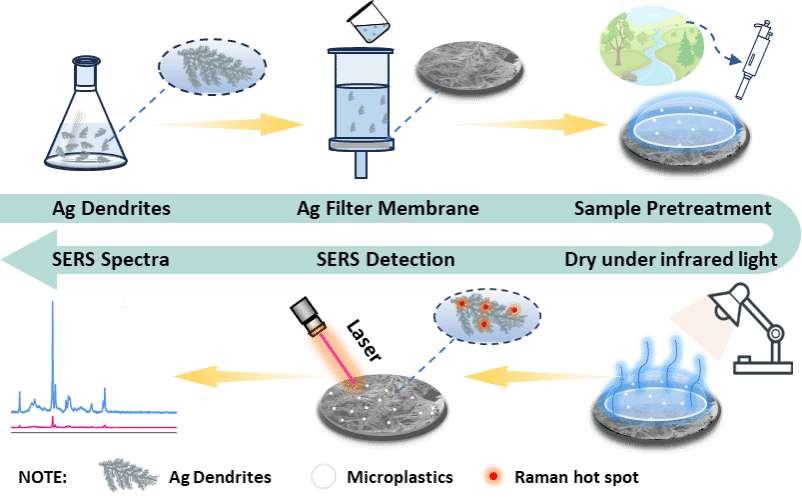
论文简介:
微塑料(microplastics, MPs)是一种新兴的污染物,广泛存在于环境水、饮用水、食品包装材料等场景中,并且可以在蔬菜、水产品等生物体内富集。已有大量研究表明,MPs可引起炎症反应和协同毒性等,对人类健康构成重大威胁。目前,表面增强拉曼散射技术(surface-enhanced Raman scattering, SERS)在MPs的分析中表现出明显优势,例如检测速度快和指纹图谱特性等,但仍存在灵敏度不够高、基底制备复杂等问题。
本研究以饮用水为对象,开发了一种具有MPs吸附能力和SERS信号增强能力的双功能复合膜,以提高MPs的SERS检测灵敏度。通过正己硫醇修饰银枝,增加其对MPs的吸附能力;辅以滤膜表面沉积的复合膜形式,提升其对待测样品中MPs的过滤和富集能力。实验结果表明,复合膜对粒径为200、500、1000 nm的聚苯乙烯(PS)MPs在10-100倍体积下表现出良好的富集效果(保留率≥98.00%)。SERS检测结果显示,在0.01-0.5 g/L浓度范围内,PS与SERS信号强度之间呈现出良好的线性关系,拉曼信号增强因子高于2.92×103,检测灵敏度可达μg/L浓度水平。同时,利用复合膜获得了聚乙烯和聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯微塑料的特征性拉曼光谱,可实现同时检测和定性分析。以上结果表明,该双功能复合膜联用SERS技术,可对饮用水样品中的痕量MPs实现快速灵敏的定性定量分析。该方法具有成本低、操作简便快捷的特点,在饮用水中MPs的污染监测方面有很大的应用潜力。
该研究成果于2024年11月发表于国际学术期刊“Journal of Hazardous Materials”。食品学院2023级研究生吴建华为第一作者,食品学院李玉芝副教授(校聘)和柳鑫教授为共同通讯作者。该研究得到十四五国家重点研发计划青年科学家项目(2022YFF1102500),国家市场监管重点实验室(动物源性食品中重点化学危害物检测技术)开放课题(KF-202203),雷竞技ray官网科研项目(2023Y11)(2024RZ011)资助。
文章链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.136394
