Toxic aldehydes in fried foods: Formation, analysis, and reduction strategies
油炸食品中的有毒醛类:形成、分析与减少策略
Abstract
During high-temperature frying, heated culinary oils undergo thermooxidative degradation of unsaturated fatty acids, resulting in the generation of harmful aldehydic lipid oxidation products. The presence of toxic aldehydes in food is a significant concern for consumers as well as industries in terms of food safety. Based on this, we conducted a search in the WoS database using “frying” and “aldehydes” as topic, combined bibliometric methods to analyze the published relevant literature, summarize the current research progress, and evaluate future development trends. This review focuses on the latest advancements in understanding aldehydes formation, harmful effects, analysis techniques, occurrence in food, and reduction approaches. Acrolein, 2,4-decadienal and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) are primarily formed through linoleic acid oxidation, while linolenic acid contributes to the production of 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal (HHE). Commonly used methods for determining aldehydes include HPLC and GC-MS. However, to meet the demand for rapid and convenient analysis, techniques such as FTIR, NMR, and electrochemical methods have gained advantages. These methods offer the potential for further optimization of experimental conditions to develop precise quantitative methods suitable for “in-situ” determination. To reduce the production of aldehydes, the application of antioxidants has been considered as an effective method and future research should focus on identifying effectively antioxidant, particularly natural antioxidants, to reduce aldehyde formation during food processing. These efforts will contribute to the production of safer and higher-quality food products.
中文摘要:
油炸食品因其独特的口感和风味深受消费者喜爱,但在高温油炸过程中,食用油会发生复杂的化学变化,产生有害的醛类物质。这些有毒醛类不仅影响食品的品质和安全,还可能对人体健康造成潜在风险。本文通过文献计量学结合文献分析方法,对油炸过程中醛类的形成机制、分析方法及减少策略进行了全面综述。研究发现,油炸过程中主要形成的有毒醛类包括丙烯醛、2,4-癸二烯醛、4-羟基-2-壬烯醛(HNE)和4-羟基-2-己烯醛(HHE)等。这些醛类的形成与油的脂肪酸组成、油炸温度和时间等因素密切相关。常用的醛类分析方法包括高效液相色谱(HPLC)、气相色谱-质谱联用(GC-MS)等,但这些方法存在样品前处理复杂、设备成本高等问题。为了减少油炸过程中醛类的生成,现有研究提出了多种减缓策略,如使用抗氧化剂、优化油炸条件和选择热稳定性更高的油品等。未来研究应进一步开发更高效、经济和准确的醛类检测方法,探索更有效的醛类控制策略,以保障油炸食品的质量和安全。
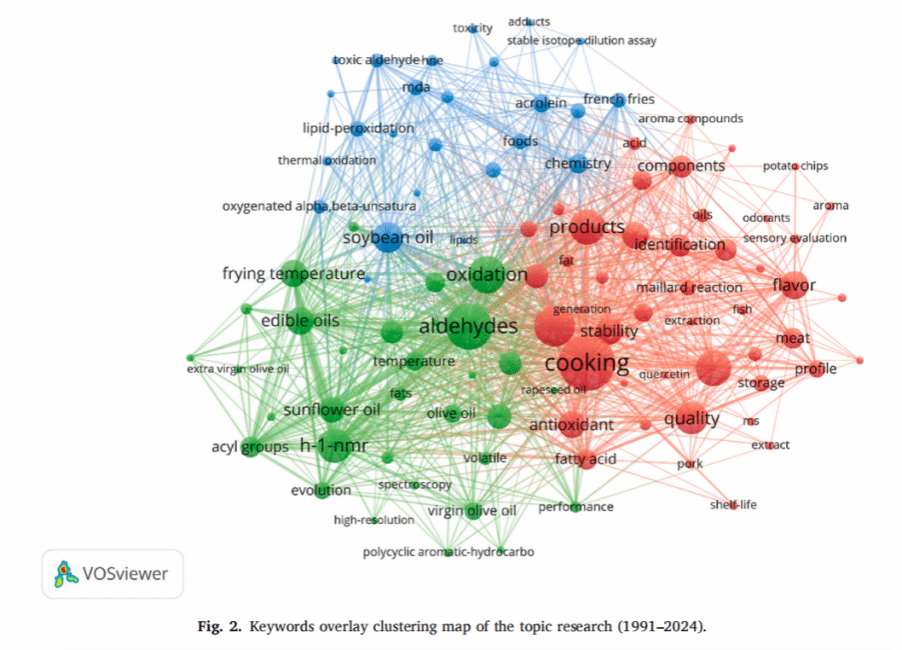
论文简介:
油炸作为一种广泛使用的烹饪方法,油炸食品因其独特的口感和风味而深受消费者喜爱。然而,随着生活水平的提高,消费者对油炸食品的质量和安全性要求也越来越高。在高温油炸过程中,食用油会发生复杂的化学变化,包括聚合、氧化和水解,产生多种降解产物,统称为总极性化合物(TPC)。其中,醛类化合物在油达到废弃标准之前大量形成,对人类健康构成显著风险。
本文通过文献计量学方法,对油炸过程中醛类的研究进行了全面总结。研究发现,富含多不饱和脂肪酸(PUFAs)的油在高温油炸过程中更容易产生高含量的醛类。常用的醛类分析方法包括液相色谱(如HPLC和LC-MS)和气相色谱(如GC-MS)。此外,FTIR、NMR和电化学方法等新兴技术为醛类的快速便捷分析提供了可能。
为了减少油炸过程中醛类的生成,研究提出了多种减缓策略,包括使用抗氧化剂、优化油炸条件(如控制油温和油炸时间)以及选择热稳定性更高的油品。这些策略的有效性得到了实验验证,为油炸食品的安全性提供了科学依据。
该研究成果于2025年3月发表于国际学术期刊“Food Control”。食品学院2023级学术型研究生呙兴阳为第一作者,油脂及植物蛋白科技创新团队殷娇娇博士为通讯作者。该项目得到了“十四五”国家重点研发计划(2023YFD2200705)和国家市场监督管理总局重点实验室(食用油质量与安全)(SYYKF202405)的项目资助。
文章链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2024.110993
