Comparison and Optimization of Different Extraction Methods of Bound Phenolics from Jizi439 Black Wheat Bran
冀紫439黑小麦麸皮结合酚不同提取方法的比较与优化
Abstract:
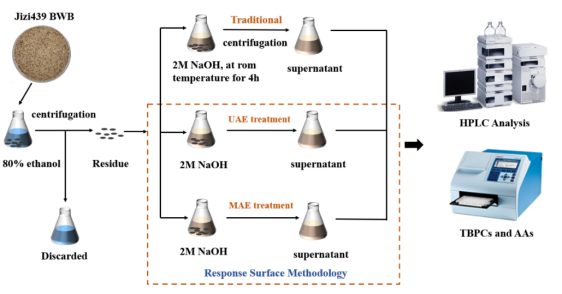
Diet rich in phenolics would potentially associate with multiple health benefits. Response surface methodology (RSM) was introduced to optimize the process of ultrasound- and microwave-assisted extraction of bound phenolics from the bran of a newly developed black wheat breeding line Jizi439 and then compared with the traditional alkaline method. The optimum conditions were found to be 66 ℃, 48 min, and power 240 W for ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE), and 120 s, power 420 W for microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), respectively. Total bound phenolic contents (TBPCs), determined by Folin-Ciocalteu reagent, were 8466.7 ± 240.9 µg gallic acid equivalents per gram (µg GAE/g) bran for UAE and 8340.7 ± 146.7 µg GAE/g bran for MAE under optimized conditions, which were both significantly higher than that of the traditional method (5688.9 ± 179.6 µg GAE/g) (p < 0.05). Antioxidant activities (AAs) were determined by DPPH and ABTS methods. UAE extracts showed the highest DPPH scavenging activity (77.5 ± 0.9%), while MAE extracts showed the highest ABTS scavenging activity (72.1 ± 0.6%). Both were significantly higher than that of the traditional method (69.6 ± 1.1% for DPPH and 65.9 ± 0.5% for ABTS) (p < 0.05). Total bound phenolics (TBPs) profiles were further analyzed by HPLC, and results indicated that ferulic acid was dominant, followed by vanillic acid and p-coumaric acid. The contents of each identified individual phenolics were significantly increased by ultrasound and microwave. In conclusion, UAE and MAE were comparable with each other in TBP yields and AAs; however, when taking operation time and energy consumption into consideration, MAE was more efficient than UAE. Our study suggested efficiency extraction methods for further use of bound phenolics as a healthy food ingredient.
中文摘要:
富含酚类物质的饮食可能会带来多种健康益处。本研究采用响应面法优化超声波和微波辅助提取冀紫439黑小麦麸皮中结合酚的工艺,并与传统的碱提法进行比较。超声波辅助提取 (UAE)的最佳工艺条件为超声温度66 ℃,超声时间48 min,超声功率240 W;微波辅助提取 (MAE)的最佳工艺条件为微波时间120 s,微波功率420 W。采用福林酚法测定总结合酚含量,在最优条件下,UAE的提取量为8466.7 ± 240.9 μg GAE/g,MAE的提取量为8340.7 ± 146.7 μg GAE/g,均显著高于传统碱提法 (5688.9±179.6 μg GAE/g) (P<0.05)。采用DPPH和ABTS测定抗氧化活性(AAs)。UAE提取物的DPPH自由基清除率最高,为77.5 ± 0.9 %,MAE提取物的ABTS自由基清除率最高,为72.1 ± 0.6%。二者均显著高于传统方法 (DPPH为69.6 ± 1.1 %,ABTS为65.9 ± 0.5 %) (P<0.05)。采用高效液相色谱对总结合酚 (TBP) 组分进行了分析,结果表明阿魏酸为主要成分,其次是香草酸和p-香豆酸。经超声波和微波处理后,各酚类物质的含量均显著增加。综上所述,UAE和MAE在TBP和AAs方面具有可比性,但从提取时间和能耗考虑,MAE比UAE更有效。这项研究为进一步利用结合酚作为健康食品成分提供了有效的提取方法。
论文主要结果:
本研究利用响应面法优化UAE和MAE的提取工艺,并比较了UAE、MAE和传统碱提法在最佳提取条件下的结合酚含量、抗氧化活性和结合酚组分。
结果表明,超声波辅助提取的最佳条件为超声温度66 ℃,超声时间48 min,超声功率240 W,微波辅助提取的最佳条件为微波功率420 W,微波时间120 s。在最佳条件下,UAE和MAE的结合酚含量和抗氧化活性接近,且均显著高于传统方法。然而,与UAE和传统方法相比,MAE具有提取时间短、能耗低的经济优势。研究表明,MAE是一种获得大量结合酚并可进一步用于食品和医药产品的有效方法。
通讯作者简介:
丁文平,教授,硕士生导师。现任国家稻米精深加工产业技术创新战略联盟副秘书长、中国粮食行业协会小麦分会常务理事、中国粮油学会理事、食品分会常务理事、发酵面制品分会副会长。雷竞技ray官网谷物加工与资源利用科研团队负责人。《中国粮油学报》、《食品科技》杂志编委。主持完成或在研国家粮食公益项目1项、国家农业成果转化资金项目2项,省部级科技项目5项,欧盟国际合作项目1项,863项目子项目1项。作为主要研究人员参与国家科技攻关项目2项,国家自然科学基金项目1项。完成华龙日清等多家国内知名企业委托的新产品研发工作。获湖北省技术发明二等奖1项、科技进步二等奖1项,河南省科技进步三等奖1项、中国粮油学会科学技术奖三等奖3项。在“ International Journal of Food Science and Technology”、《农业工程学报》、《食品科学》、《中国粮油学报》等期刊上发表科研论文40余篇,其中三大索引6篇,参加ICC(世界谷物科技组织)国际学术会议并交流英文论文2篇,主编或参编《粮油副产品开发技术》、《谷物加工工程》等3部著作共30余万字。
共同第一作者简介:
陈曦,博士,副教授,毕业于美国堪萨斯州立大学 (Kansas State University)食品营养与健康系,主要从事谷物营养及功能活性评价和谷物功能性食品开发研究。
孙奎杰,Raybet在线官网20级硕士研究生,专业为生物与医药,研究方向为谷物资源开发与利用,以第一作者发表SCI论文1篇,申请国家发明专利1项。
